In CRM 2013 Microsoft introduced many more interesting
features one of them being Business Rules. Business Rules is a way to provide
custom business logic through a simple to use UI and eliminate the need to write
scripts to handle such UI driven business logic. Examples of such business
logic includes enable/disable or show/hide logic or business required or set
the value of one field based on the value entered by user in another field.
How to create Business Rules in CRM 2013
Once you click on “New Business
Rule” it will open following window.
Let us look at each of the fields available on this screen.
Scope: Using scope
you can define the Forms that you would like to apply the business logic on.
You can choose a single or all forms to apply this business rule on.
Name: Provide a
descriptive name for the rule.
Conditions: In
this section you can specify the conditions if any to check. You can provide
multiple conditions and currently all conditions are combined using “AND”. It
does not provide support for “OR”.
Field
: Select the Field for comparison. This will list out all the fields from
selected entity.
Operator
: Select the comparison operator.
Type
: it allow us to specify the type of data with which comparison should be done.
It has options as Field and Value as shown below.
Once condition is set click on tick mark button as shown
above so it will save the condition.
Now as you can see in below example we have set Business
Rule name as “Account number required” and condition as “If
Relationship Type equals Customer” and “Account Number does not contain data”
Going further after specifying condition now set the action need to be
performed when condition is true.
Action : it allows us to set the actions which will
get triggered when condition is true.
1. Show error message: if condition is true
and if you set action as “Show error message” it will show/throw error. Here
you can select the field on which you would like to set error message and give
specific error message. And save those changes.
It will show error as follows.
2. Set field value: if condition is true and
if you set action as “Set field value” it will set specific field to default
field value or to another field value. This could be used in scenarios where
the Probability % is driven by the sales stages on opportunity.
For example, if you have sales
stage selected as “Qualify” then you can set probability of that opportunity as
30, If sales stage is “Develop” then probability is 50, If sales stage is
“Propose” then probability is 80 and when sales stage is “Close” then
probability is 100.
Note: consider for each
condition you need to create different Business Rule. then only it will set
different values for different sales stages.
It will set value as
follow.
3. Set business required: if condition is
true and if you set action as “Set business required” it will set another field
as “Business Required” or “Not Business Required”. As shown in
below select field which you would like to set business required and then set
status as per requirement. Click on save.
It will set field business
required as follow. Once you select Relationship type as “Customer”, it will
set Account Number as Business Required.
4. Set visibility: if condition is true and
if you set action as “Set visibility” it will either hide the field or show the
field on form. As shown below select field for which you would like to set
visibility then select the status of field either “Show field” or “Hide
field”. And save those changes.
By default it will show Account number field on
account form but once you select relationship type as Customer it will get hide
as shown below.
5.
Lock or unlock the field: if condition is
true and if you set action as “Lock or unlock the field” it will either lock
the field or unlock the field on form. As shown below select the field and then
set its status either “Lock” or “Unlock”.
By default the Account number field
is Unlocked but once you select Relationship type as customer, the Account
number field get Locked as shown below.
Note: There is no way to provide for an “Else”
condition right now. So if you would like the action to differ when the
relation type is “Customer” and when it is something else, you need to create
another rule for the else condition. If another rule is not created and you
change the value of the relation type from Customer to something else, the
error being displayed on Account number would not be immediately refreshed
similar to onchange scripts written with if.. else condition to handle
immediate updates.
After this you can specify the Description about the
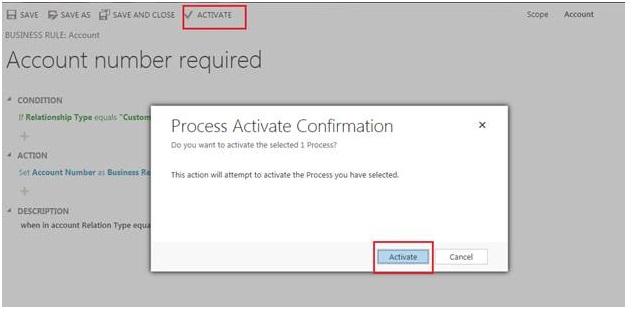
rule as shown in below screen shot. Click on save and Activate the Rule.
Once you click on Activate button it will prompt for Process
Activate Confirmation window here select Activate.
Once Rule is activated its status is changed from draft to
Activated as shown below.
Note :
1) consider whenever you require to do changes in rule
you need to first deactivate it and then do the changes, save those changes and
Activate that rule again.
2) Business rules being a part of entity customization
can be shipped along with the entity.
3) Since the tablet UI is rendered based on the entity
forms defined, the business rules would also be applied on Tablet devices.
Conclusion
Business Rules is a
very strong tool in the hands of System Administrators where by they can easily
implement custom UI logic. The fact that rules defined here are applied
universally on all UI interfaces web client/outlook client/Tablet client makes
it easier to implement standard UI behavior across all devices.